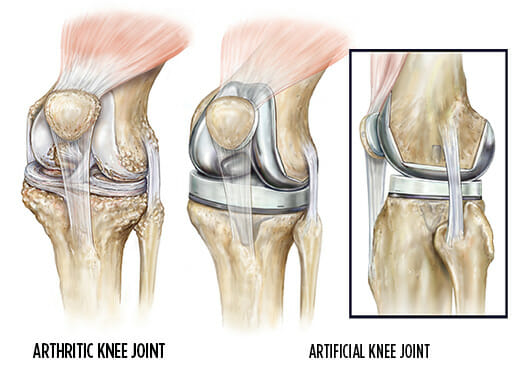
Total Knee Replacement (TKR), also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure that replaces the entire knee joint with an artificial prosthesis to relieve pain and improve function. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals suffering from severe knee pain and limited mobility due to conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis or traumatic injury.
Why it's done
TKR is not always the first option for treating knee pain. Non-surgical treatments, such as physical therapy, medication, weight management and knee injections, are often tried first. However, when these methods fail to provide sufficient relief, TKR may be recommended under the following circumstances :
Severe pain that interferes with daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs or getting up from a chair.
Persistent knee swelling or inflammation that does not improve with conservative treatments.
Significant loss of knee mobility, making it difficult to bend or straighten the leg.
Advanced degeneration due to osteoarthritis or other joint diseases.
Deformities such as bowlegs or knock-knees that impact alignment and stability.
The Procedure
A Total Knee Replacement surgery typically involves the following steps :
Preoperative Preparation : Patients undergo a thorough evaluation, including imaging tests like X-ray or MRI or Citi scan, blood work and consultations to ensure they are suitable candidates for surgery. Physical preparation, such as strengthening exercises, may also be recommended.
Anesthesia : The procedure is performed under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia (spinal or epidural), depending on the patient's medical condition and Anaesthesiologist preference.
Incision : A surgical incision is made at the front of the knee to access the joint.
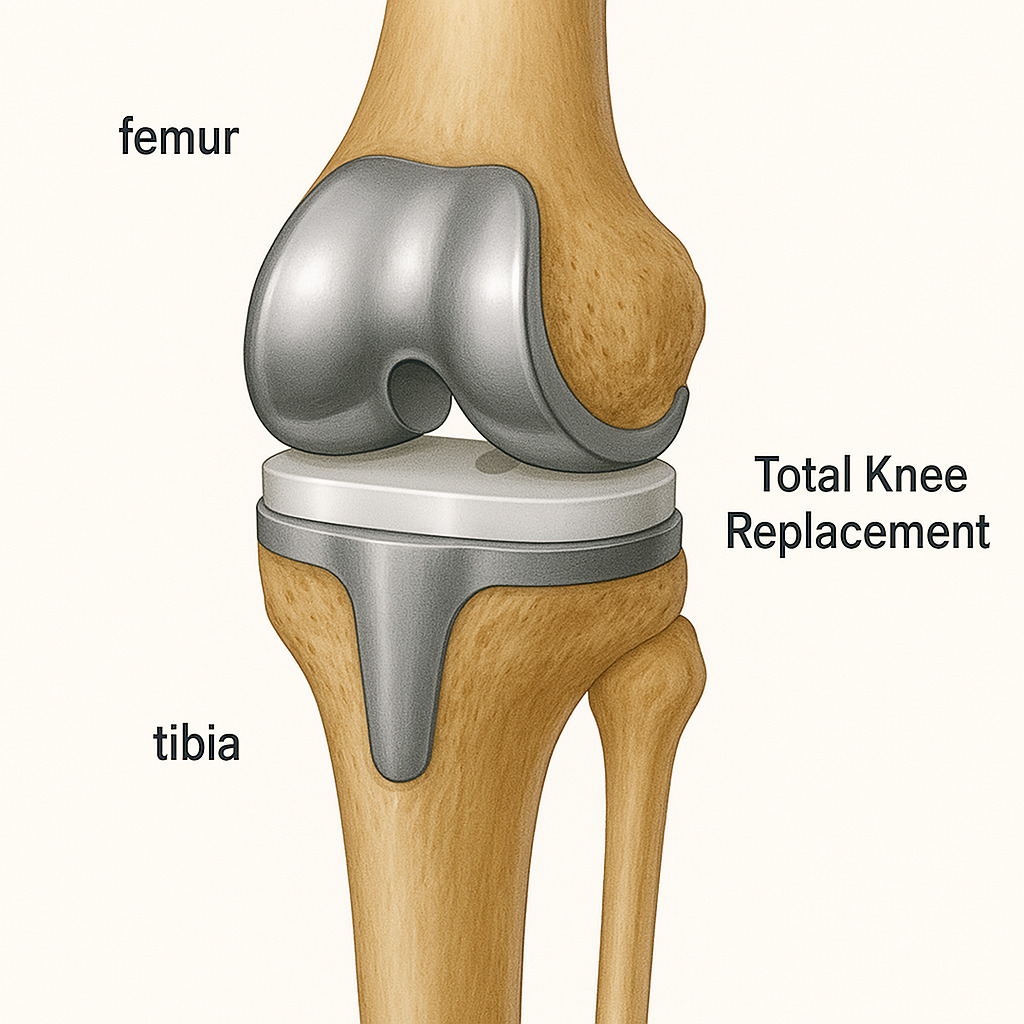
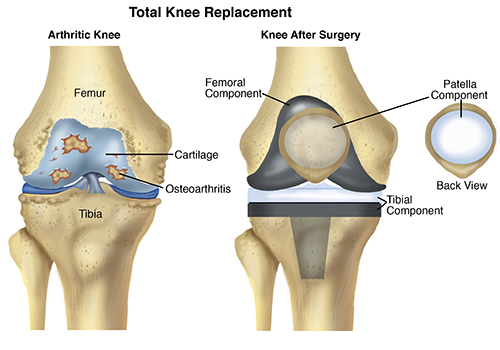
Resurfacing : Damaged bone and cartilage are removed from the femur, tibia and patella. Metal components are then attached to the ends of these bones and a plastic spacer is placed in between them to create a smooth surface for movement.
Closure : The incision is closed with sutures or staples; the knee is bandaged.
Postoperative Care : Patients are monitored in recovery room for pain management and overall health stabilization.
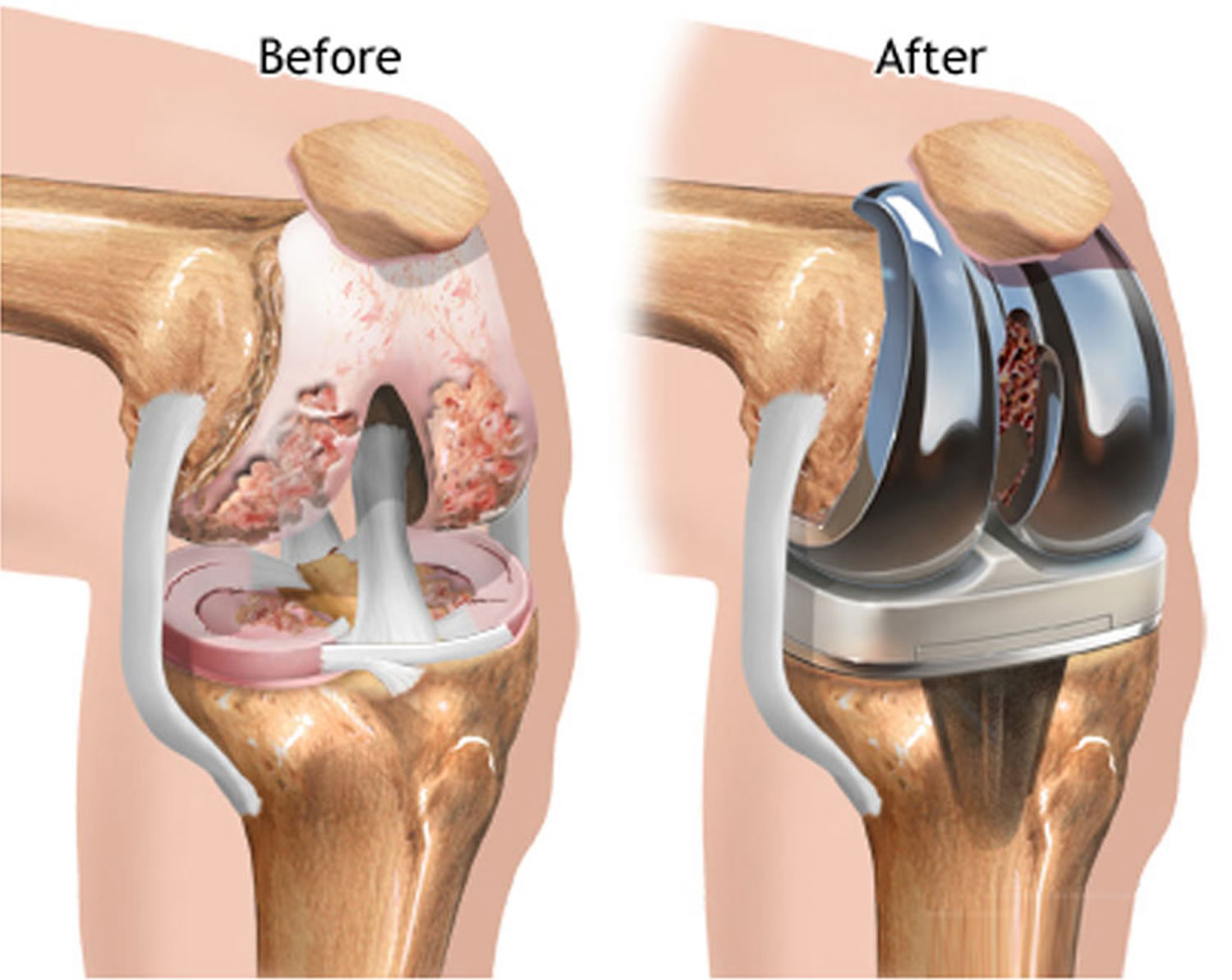
Benefits of Total Knee Replacement
TKR offers several advantages, including :
Pain Relief : The surgery effectively eliminates or significantly reduces chronic knee pain.
Improved Mobility : Patients regain the ability to perform daily activities and enjoy an active lifestyle.
Enhanced Quality of Life : The procedure allows individuals to participate in hobbies and social interactions without discomfort.
Durability: Modern implants can last 15-20 years or longer, depending on activity levels and overall health.
Risks
Knee replacement surgery, like any surgery, carries risks. They include :
Blood clots. Surgeons often recommend blood-thinning medicines to prevent this risk. The most common location for blood clots is in the leg. But they can travel to the lungs and become deadly.
Nerve damage. Nerves in the area where the implant is placed can be injured. Nerve damage can cause numbness, weakness and pain.
Infection. Infection can occur at the incision site or in the deeper tissue. Surgery is sometimes needed to treat an infection.