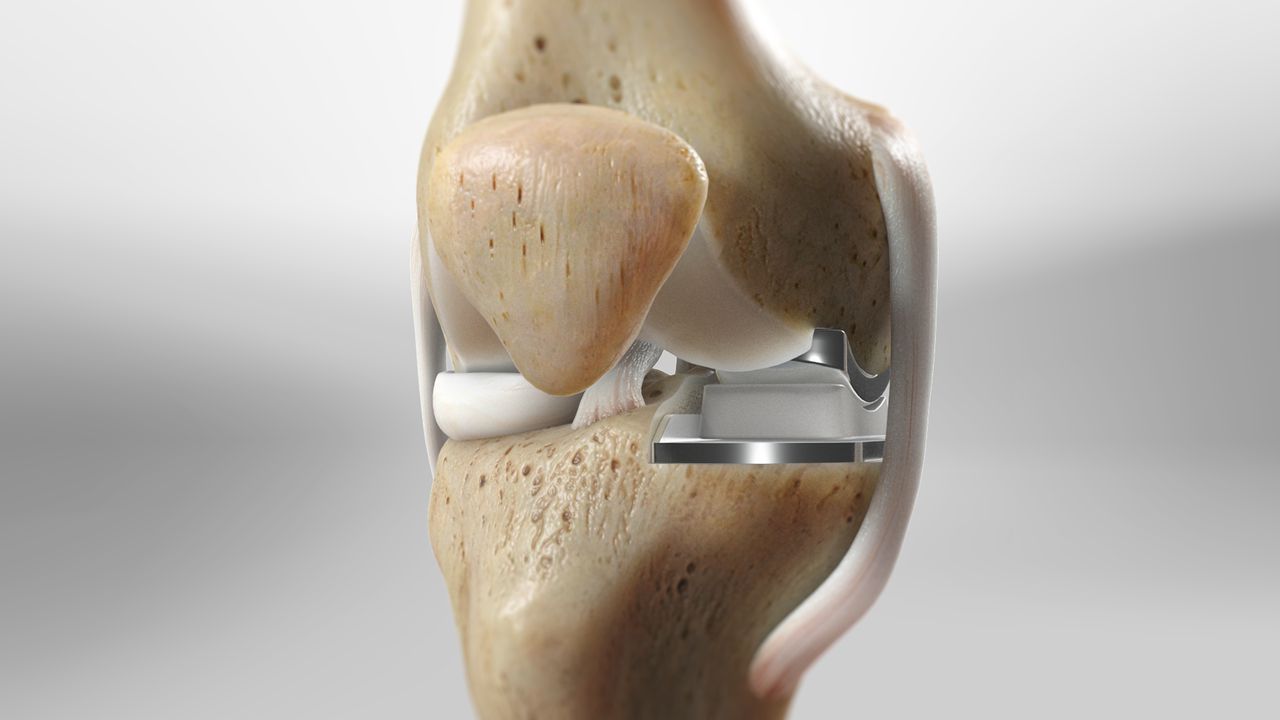
Partial knee replacement (PKR), also known as unicondylar or unicompartmental knee replacement, is a surgical procedure that replaces only the damaged portion of the knee joint, while preserving the healthy parts. Unlike total knee replacement, PKR focuses on restoring function by targeting one or two specific compartments of the knee.
Who is a candidate for partial knee replacement ?
Most people who choose to have a partial knee replacement have osteoarthritis. A healthcare provider might recommend a partial knee replacement if you have severe symptoms that don't get better after trying nonsurgical treatment.
What is the best age for a partial knee replacement ?
Orthopedic surgeons often perform partial knee replacement in younger patients — those under age 50 — rather than total knee replacement. Yet it can be stressedthat there is no precise age cutoff for this surgery; as it is based on a patient's overall health and severity of arthritis.
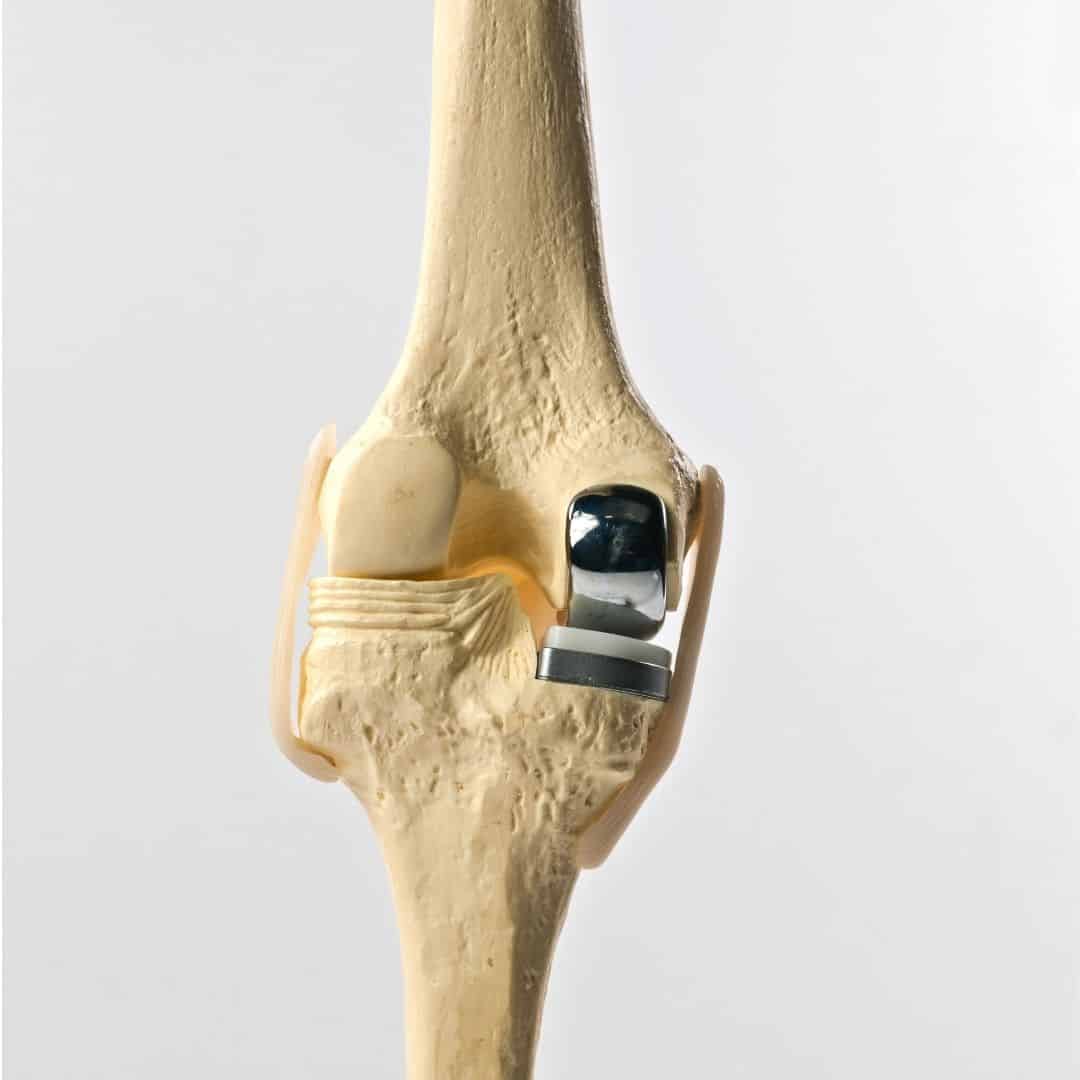
The Procedure
A partial knee replacement procedure involves surgically removing the damaged cartilage and bone from only one or two compartments of the knee joint and then replacing them with artificial implants. This is a less invasive option than a total knee replacement and it preserves more of the natural knee joint.
Anesthesia : Before surgery, you will receive anesthesia to numb your body and ensure you don't feel any pain. This can be general anesthesia (putting you to sleep) or regional anesthesia (numbing you from the waist down).
Incision : The surgeon will make a small incision, typically 3 to 5 inches long over the knee joint.
Compartment Examination : The surgeon will then assess all three compartments of the knee joint (the medial, lateral and patellofemoral compartments) to determine if a partial or total replacement is needed.
Removal of Damaged Tissue : If the damage is limited to one or two compartments, the surgeon will remove the damaged cartilage and bone from those specific compartments.
Closure : The incision is then closed with stitches or staples.
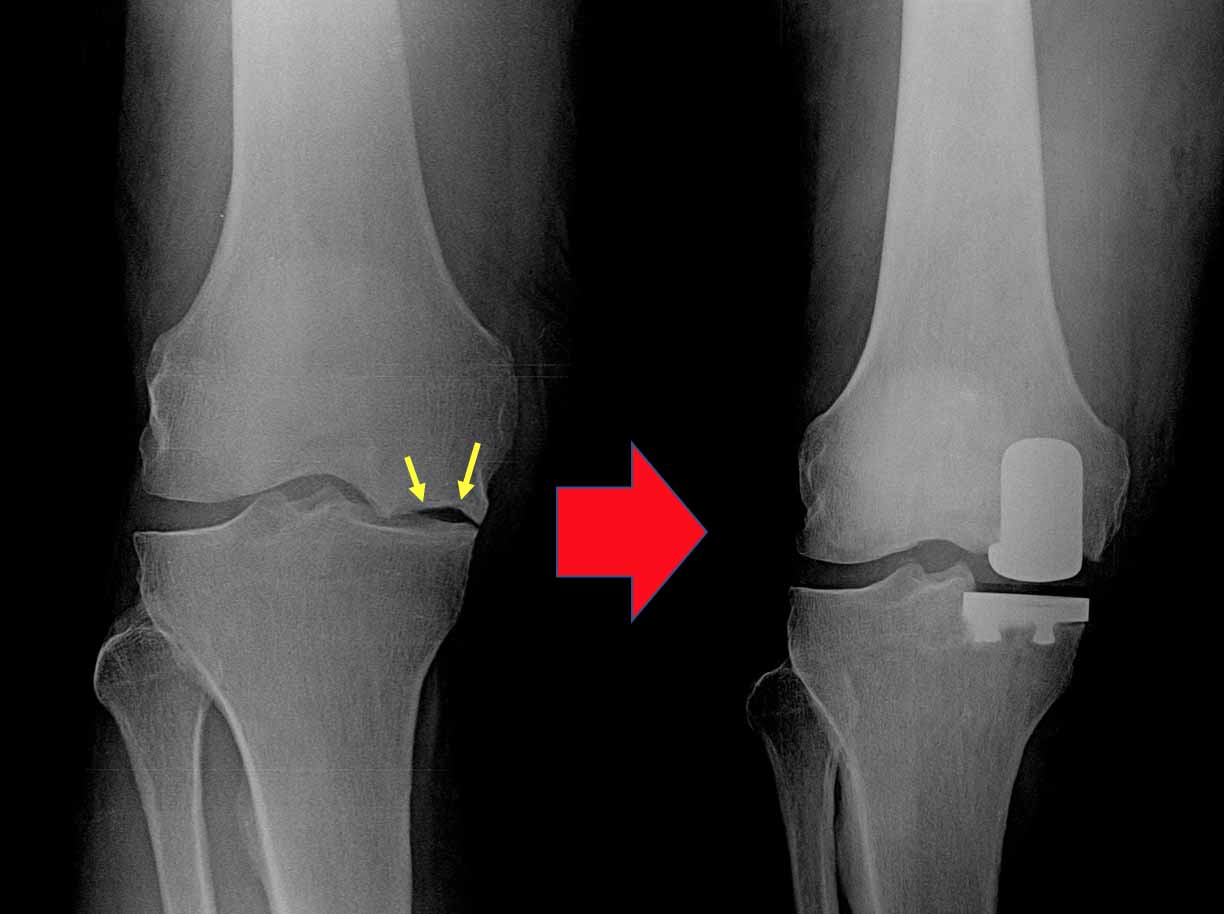
Benefits of partial knee replacement
Here's a more detailed look at the benefits :
Faster Recovery : Partial knee replacement generally requires smaller incisions and preserves more of the knee's natural structures leading to a quicker recovery time and shorter hospital stay.
Natural Knee Feel : Since only the damaged part of the knee is replaced, patients often experience a more natural knee movement and function after surgery.
Lower Risk of Complications : The less invasive nature of partial knee replacement can reduce the risk of complications like infections and blood clots.
Quicker Return to Activities : The faster recovery time allows patients to return to work and daily activities, including sports more quickly.
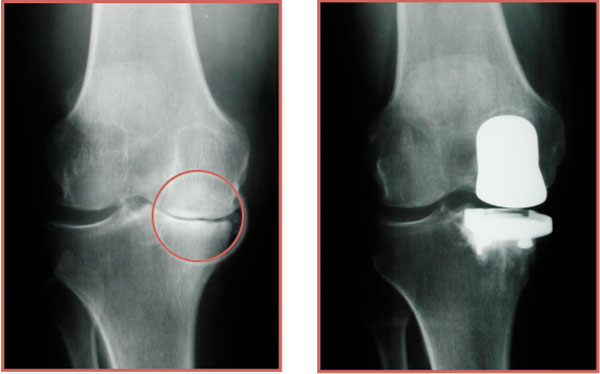
Risks
Partial knee replacements, while beneficial for some, also carry potential drawbacks. These include a higher revision rate compared to total knee replacements, the possibility of arthritis developing in the remaining joint and the potential for the implant to loosen or wear down over time.
Partial knee replacements may have a higher rate of requiring revision surgery compared to total knee replacements.
This means a second surgery might be needed to address issues like implant loosening or failure.
Since only a portion of the knee joint is replaced, there's a risk that arthritis could develop or worsen in the remaining, unreplaced part of the knee.
The prosthetic implants in a partial knee replacement can loosen over time, especially if they aren't properly attached to the bone.